Chemical pumps are designed to deal with hazardous, corrosive compounds. They contain corrosion-resistant materials. Manufacturers use chemical pumps to process bleach, acid, resin, commercial or industrial abrasives, and corrosive liquids. In a chemical centrifugal pump, rotating impellers push the liquid to specific speeds. Centrifugal force in the pump produces the liquid’s velocity. When the amount of flow is more than the required pressure, chemical pumps are used for chemicals with viscosities similar to water. Read More…
At Puffer Sweiven Rotating Equipment, we take pride in delivering dependable centrifugal pump solutions that keep critical operations running smoothly across process industries. We draw on decades of field experience and technical expertise to help our customers select, install, and maintain centrifugal pumps that meet demanding performance, reliability, and efficiency requirements.
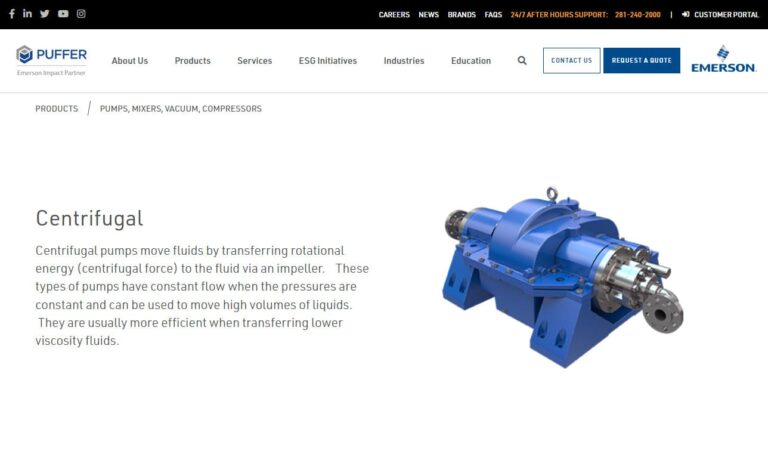
Ryan Herco Flow Solutions is a leading national distributor for fluid handling products. Our family of products include; Flowmeters, sensors, instrumentation tubing and hose, process pipe and fittings, valves, pumps, filters and filter systems, storage and drums, and corrosion resistant structural products. We have 29 U.S. Service Centers ready to serve you.
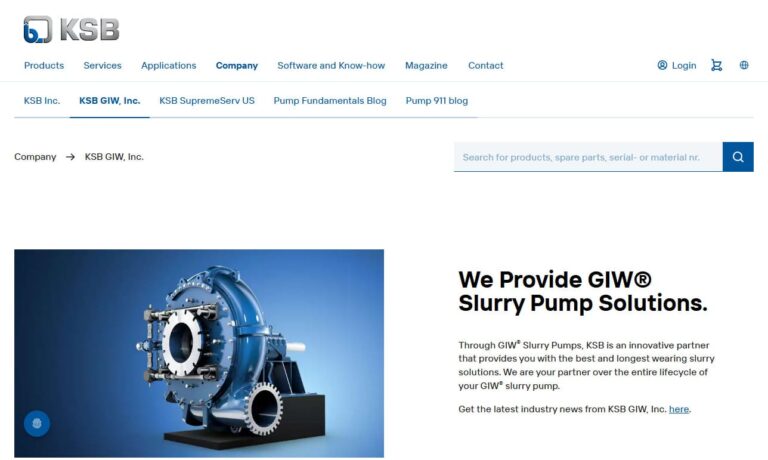
Centrifugal slurry pumps are not a necessity for everyone. However, when one is in need of such, they seek us. We manufacture pumps to handle coarse or fine particles, wastewater with solids, highly corrosive slurry, abrasive slurry or basically any water mixture with insoluble matter.
At Xylem, we take pride in advancing water technology through innovation and engineering excellence. Our centrifugal pumps are designed to deliver dependable, efficient performance across a broad range of industries and applications.
We are Pacer Pumps, a leading manufacturer of pumps and pumping solutions for a variety of applications. With over 50 years of experience in the industry, we are committed to providing our customers with high-quality, reliable products and exceptional service. At Pacer Pumps, we offer a wide range of pumps to suit a variety of needs, including centrifugal, self-priming, and hydraulic-driven pumps.
Flowserve centrifugal pumps are key components in the worldwide oil and gas, hydrocarbon and chemical processing, power generation and water resources industries. Our pumps comply either with ISO, ASME or API standards, and are available in various designs to meet the stringent demands of chemical handling applications. Visit our website today to learn more about our line of products.
For over 150 years, we have manufactured centrifugal pumps for industrial global markets. We offer hard metal, rubber lined, vertical cantilever, submersible and self priming pumps. Our solutions lower costs of the pump life cycle for fluid handling problems. ISO 9001 certified company.
At Baker Hughes, we design and manufacture centrifugal pumps that deliver exceptional reliability and efficiency across a wide range of industrial and energy applications. We engineer our pump systems to move fluids safely and consistently under the most demanding conditions, from upstream oil and gas operations to power generation and process industries.
More Chemical Pump Manufacturers
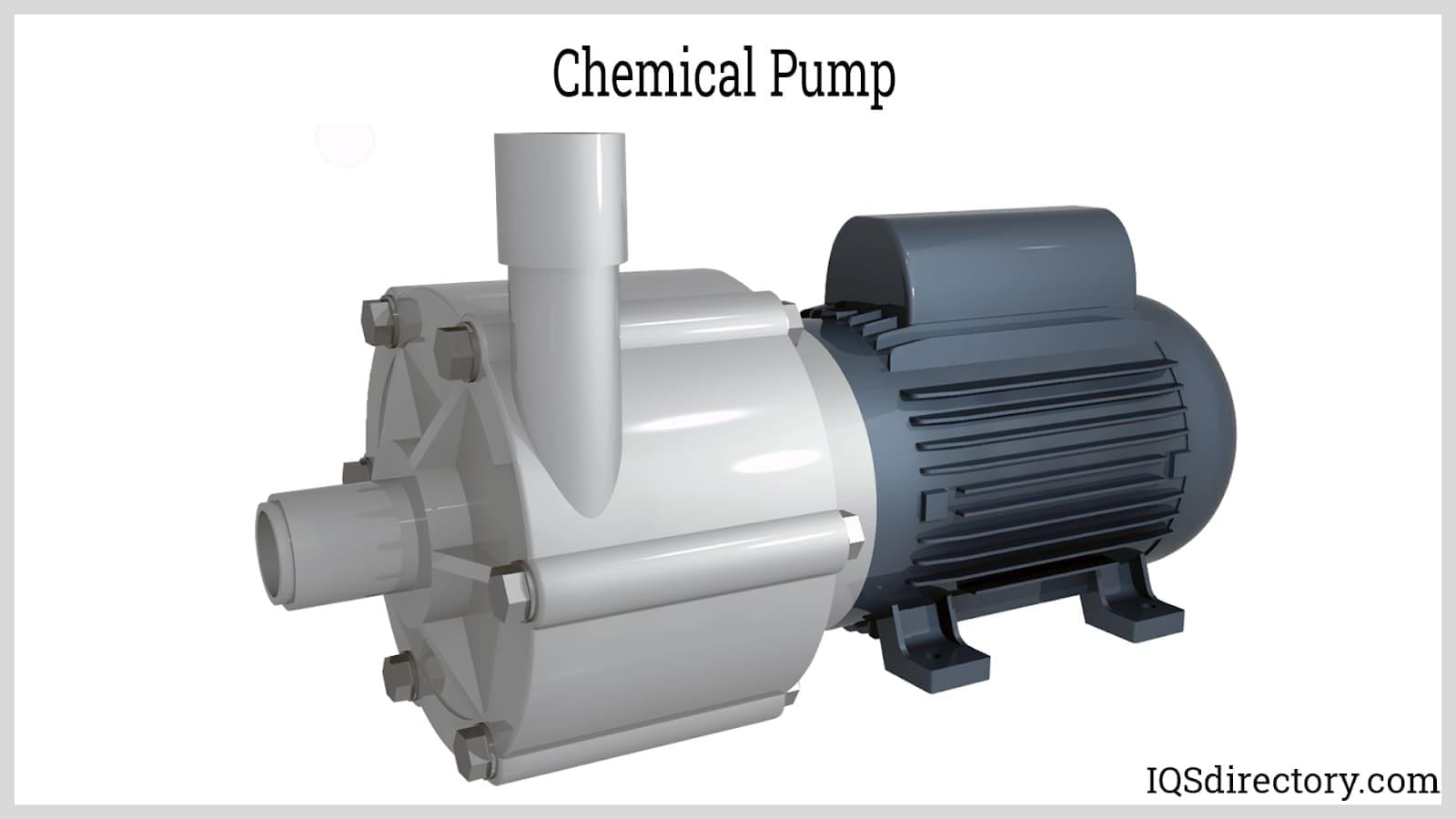
When handling aggressive, corrosive, or hazardous chemicals in industrial environments, using a standard pump can result in significant damage such as brittleness, swelling, dissolution, leaks, or even catastrophic failure. Chemical pumps are engineered specifically for chemical processing applications, with careful attention given to construction materials, compatibility with various chemical concentrations, and temperature tolerances. These specialized pumps play a critical role in industries such as chemical manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, water treatment, oil & gas, food processing, and more.
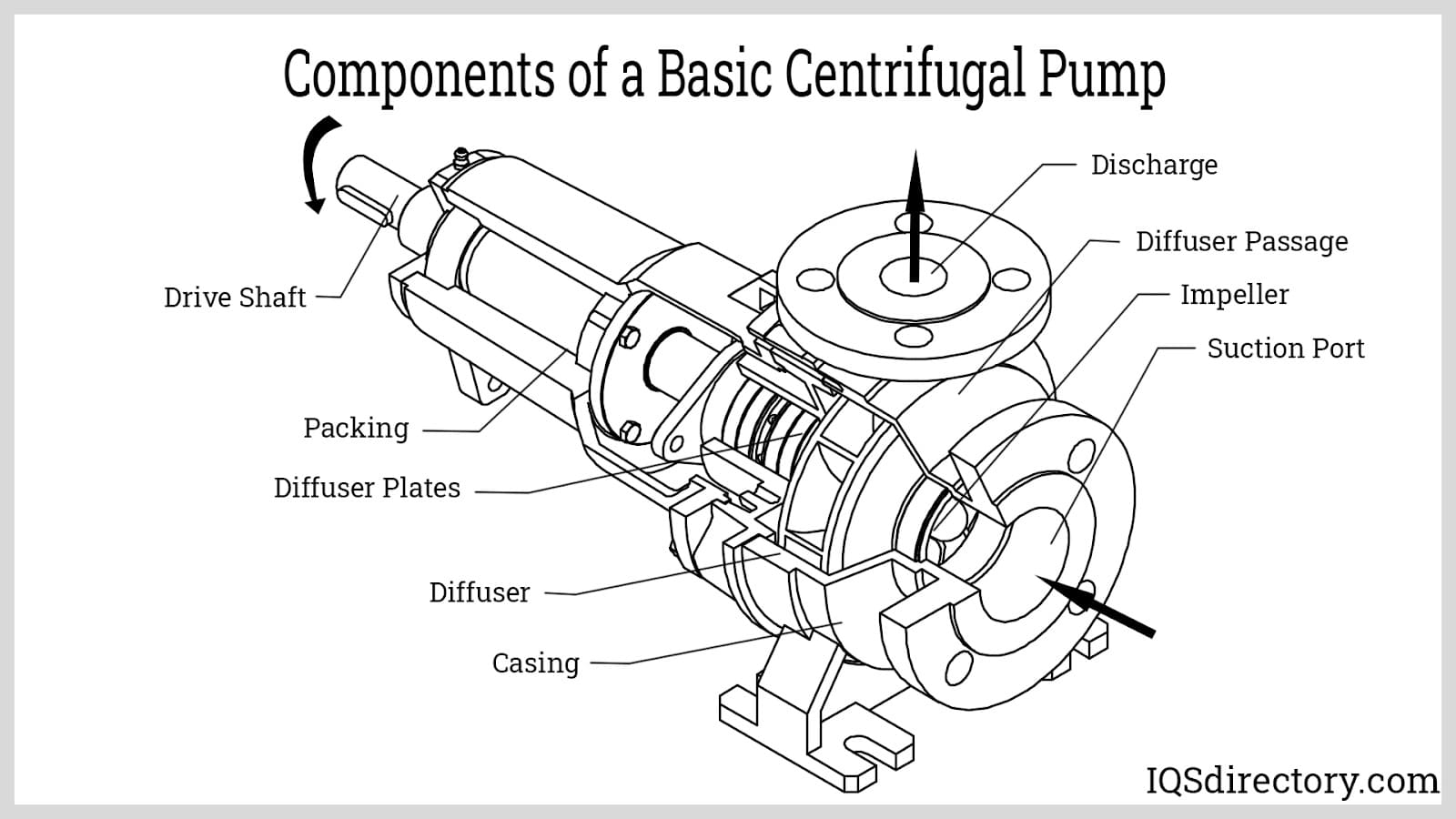
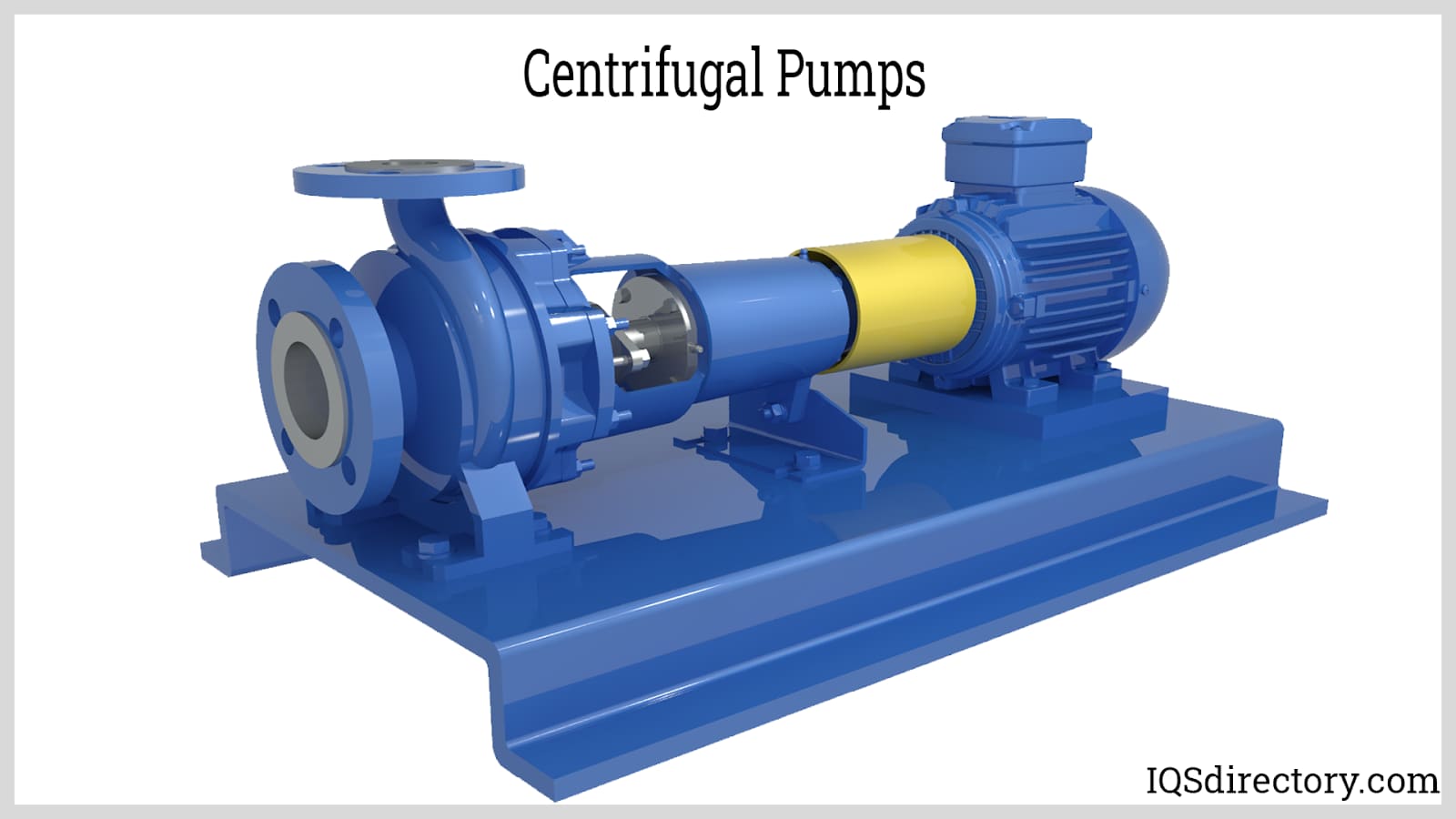
Every centrifugal pump, including those designed for chemical use, consists of key mechanical components that enable efficient fluid transfer. The fundamental parts of a centrifugal chemical pump include:
- Sealing mechanism (mechanical seal or gland packing)
- Shaft
- Impeller
- Delivery pipe
- Casing
- Suction pipe
Working Principle of a Chemical Pump
The core function of a chemical centrifugal pump relies on an internal rotating impeller. This impeller is directly coupled to the pump’s motor, typically through an aperture in the pump housing. To prevent potentially hazardous leaks, a robust mechanical seal—commonly fabricated from ceramic, silicon carbide, or carbon rings—is installed at the aperture. During operation, one ring spins with the shaft while the other remains stationary, allowing a thin lubricating layer of fluid to circulate between the faces and maintain seal integrity.
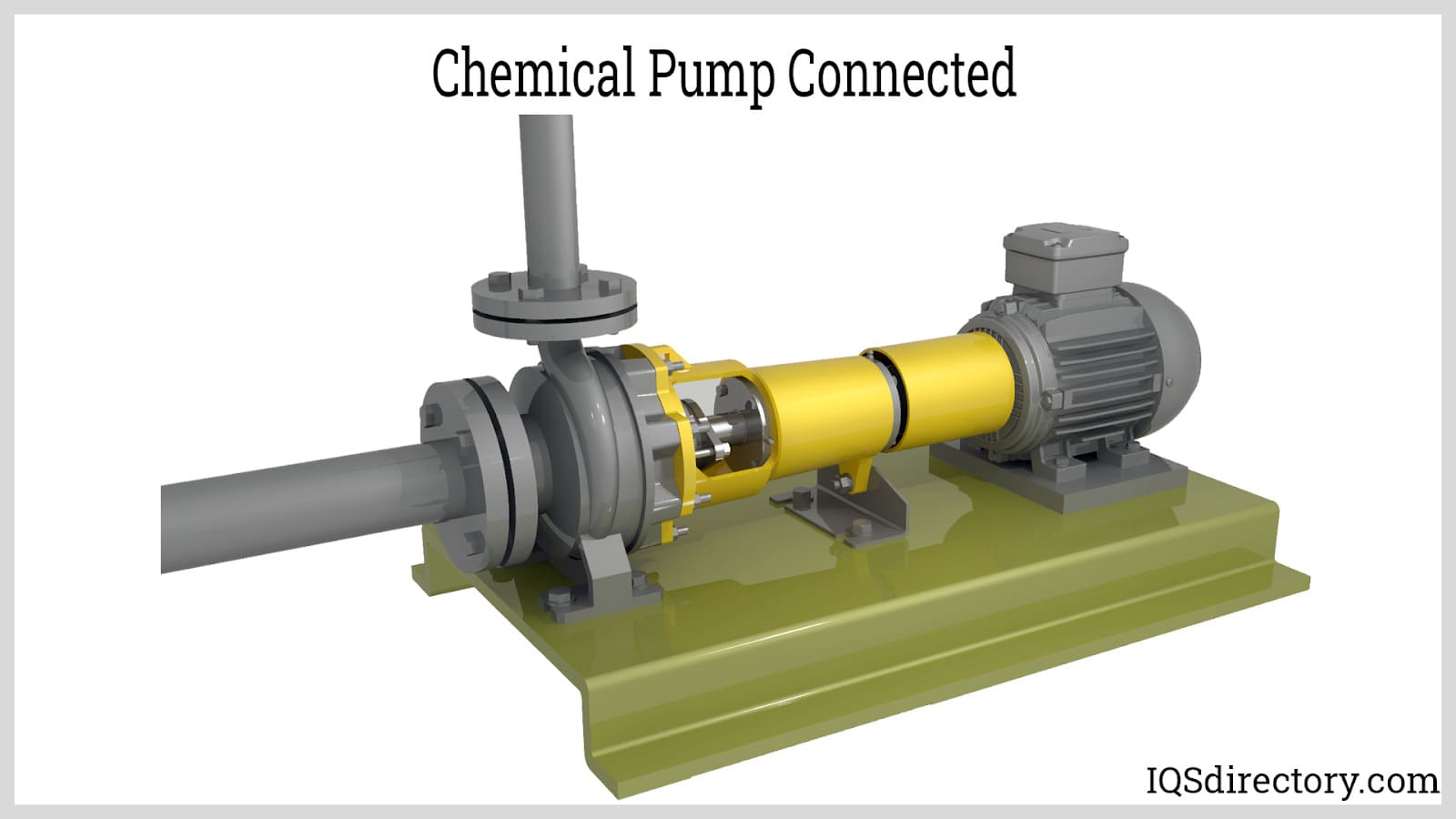
How does a chemical pump prime and move fluid? Before startup, the pump body must be filled with liquid to ensure a proper seal and efficient operation. When activated, the impeller rapidly spins, imparting kinetic energy to the fluid and causing it to move outward due to centrifugal force. This movement drives the liquid into the diffusion chamber of the pump casing, where its velocity is gradually reduced, and its pressure increases.
The continuous action of the vanes ensures no vacuum depression occurs at the pump center, supporting uninterrupted fluid intake. Atmospheric pressure then pushes more liquid into the suction pipe, enabling a consistent flow from the source (such as a storage tank or process vessel) through the pump and into the delivery system.
Types of Chemical Pumps: Matching Technology to Application
Not all chemical transfer applications are alike. The choice of chemical pump type depends on fluid properties, required flow rates, pressure, and system configuration. Here are some common types:
- Centrifugal Chemical Pumps: Ideal for low-viscosity, clean fluids. These are the most widely used due to their simplicity, efficiency, and ability to handle large volumes.
- Magnetic Drive Pumps: Utilize a magnetic coupling to eliminate shaft seals, making them leak-free and optimal for toxic, volatile, or environmentally hazardous chemicals.
- Diaphragm Pumps: Good for abrasive, viscous, or shear-sensitive fluids, and for applications where dry running may occur.
- Peristaltic (Hose) Pumps: Excellent for metering and dosing precise chemical quantities, especially with aggressive or slurries.
- Gear Pumps: Suitable for transferring high-viscosity fluids and providing accurate, pulseless flow.
- Vertical Chemical Pumps: Designed for sump or tank applications where the pump is partially submerged.
Not sure which pump is right for your application? Contact a chemical pump specialist for expert guidance based on your specific chemical compatibility, flow requirements, and operational environment.
Key Considerations When Selecting a Chemical Pump
Choosing the optimal chemical centrifugal pump or any industrial chemical pump requires detailed evaluation of your process needs. To ensure safety, reliability, and regulatory compliance, consider the following factors:
- Chemical Compatibility: What chemicals (acids, bases, solvents, oxidizers, slurries) will the pump handle? Use compatibility charts to select the correct wetted materials (such as PTFE, PVDF, stainless steel, Hastelloy, or polypropylene).
- Fluid Temperature: Verify the pump’s material and seal can withstand both normal and peak process temperatures.
- pH Value and Corrosivity: Highly acidic or alkaline fluids require corrosion-resistant pumps and seals.
- Viscosity and Density: High-viscosity or dense fluids may need positive displacement or specialized chemical transfer pumps.
- Presence of Solids or Particulates: Select pumps that can handle slurries or abrasive particles without excessive wear.
- Flow Rate and Pressure Requirements: Define maximum and minimum operating ranges for both to ensure efficient system performance.
- Seal Type: Choose between mechanical seals, magnetic drives, or sealless designs depending on leak prevention and maintenance needs.
- Installation Environment: Consider factors such as hazardous area classification, space limitations, and ease of access for maintenance.
- Certification & Compliance: Ensure compliance with industry standards such as ANSI, ISO, ATEX, or FDA where applicable.
Looking for guidance on chemical pump sizing or selection? Try searching: “How do I size a chemical pump for my application?” or “What materials are best for chemical resistance in pumps?” to explore more resources and technical data.
Applications: Where Are Chemical Pumps Used?
Chemical pumps are indispensable across a wide spectrum of industries and processes. Typical applications include:
- Chemical Manufacturing and Processing: Transferring raw chemicals, intermediates, and finished products in batch or continuous operations.
- Pharmaceutical Production: Accurate dosing, blending, and transfer of active ingredients and solvents.
- Water and Wastewater Treatment: Metering corrosive reagents such as chlorine, sodium hypochlorite, or caustic soda.
- Oil & Gas: Handling acids, amines, and solvents in upstream, midstream, and downstream operations.
- Mining: Pumping lixiviants, acid leachates, and abrasive slurries.
- Food & Beverage Processing: Safe transfer of flavorings, additives, and cleaning chemicals, with sanitary pump options available.
- Pulp and Paper: Circulation of bleaching agents, caustics, and process chemicals.
- Power Generation: Dosing water treatment chemicals for boiler and cooling systems.
- Laboratory and Pilot Plant: Precise transfer of small-volume, high-purity, or hazardous chemicals.
Interested in industry-specific solutions? Search for: “Best chemical pumps for [your industry/application]” to compare product features, case studies, and reviews.
Advantages of a Centrifugal Chemical Pump
Corrosive Resistance
Centrifugal chemical pumps are manufactured using advanced corrosion-resistant materials—such as fluoropolymers (PTFE, PVDF), high-alloy stainless steels (316SS, Hastelloy), and engineering plastics (polypropylene, ETFE)—to withstand harsh chemicals and aggressive cleaning agents. This durability makes them ideal for continuous duty in demanding environments, ensuring pump longevity and minimizing unexpected downtime. These pumps help chemical manufacturers and processors achieve a high return on investment by reducing replacement frequency and maintenance costs.
Reliable Performance
With robust designs honed over decades, chemical centrifugal pumps are known for their dependable, long-lasting operation. Their straightforward mechanics and proven engineering minimize wear and tear, providing consistent performance even in 24/7 industrial processes. Reliability is critical where process interruptions can lead to costly production delays or safety hazards.
Energy Efficiency
Compared to other pump technologies, centrifugal chemical pumps are typically more energy-efficient, offering reduced operational costs and lower per-unit energy consumption. Their streamlined hydraulic design and ability to handle large volumes with minimal energy input make them an excellent choice for facilities running multiple pumps or requiring continuous operation. Investing in energy-efficient pumps also supports sustainability and environmental goals.
Easy Maintenance
Chemical centrifugal pumps are designed for ease of maintenance, featuring fewer moving parts and simplified construction. Routine servicing—such as seal inspection, bearing replacement, or impeller cleaning—can be carried out quickly, reducing labor costs and process downtime. Many models offer modular components for rapid replacement, streamlining repair and minimizing inventory requirements.
Flexible and Customizable
Chemical pumps are available in a wide range of sizes, materials, and configurations to meet diverse process needs. Whether you require a compact pump for a laboratory skid or a high-capacity model for a chemical plant, manufacturers offer customizable solutions for flow rate, pressure, material compatibility, and control features. Options such as explosion-proof motors, smart sensors, and automated controls further enhance pump safety and efficiency.
Cost of Chemical Pumps: Total Cost of Ownership
When evaluating chemical pumps for sale, it’s essential to look beyond just the purchase price. The total cost of ownership (TCO) includes installation, commissioning, energy consumption, maintenance, downtime risk, and eventual replacement or disposal. Choosing the right pump can lead to significant cost savings over its lifetime by reducing unplanned outages, minimizing repair frequency, and optimizing energy use.
Looking to compare chemical pump prices? Search for: “chemical pump cost calculator” or “chemical pump ROI analysis” to find tools and worksheets for TCO estimation.
How to Find the Right Chemical Pumps Supplier or Manufacturer
To ensure the best value and performance when sourcing chemical pumps for your facility, it is recommended to compare offerings from multiple reputable chemical pump suppliers and manufacturers. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
- Research at least 5–6 leading chemical pump manufacturers using directories or supplier lists.
- Review each company’s profile, focusing on their expertise, product range, and industry certifications.
- Visit their websites (many directories offer preview tools) to explore detailed technical data, application guides, and customer testimonials.
- Use RFQ (Request for Quote) forms to contact multiple companies with your requirements for a tailored proposal.
- Evaluate after-sales support, warranty terms, and availability of spare parts and service centers.
- Consider the supplier’s experience with your industry and their ability to offer custom solutions or technical support.
Ready to request quotes or compare chemical pump suppliers? Use our supplier directory and RFQ form to simplify your procurement process and connect with leading manufacturers.
Frequently Asked Questions About Chemical Pumps
What is the best material for a chemical pump?
The best material depends on the chemicals being transferred. Common choices include PTFE, PVDF, polypropylene, stainless steel, and Hastelloy. Always consult a chemical compatibility chart to confirm suitability for your application.
How do I size a chemical pump?
Pump sizing should be based on required flow rate, discharge pressure, fluid properties, and system configuration. Use pump curves provided by manufacturers and consult with a pump engineer or supplier for precise recommendations.
Can chemical pumps handle solids or slurries?
Some chemical pumps, such as diaphragm or peristaltic pumps, can handle slurries or fluids with suspended solids. Centrifugal pumps are generally best for clean, low-viscosity liquids but can be configured for light slurries with appropriate design.
Are chemical pumps safe for hazardous locations?
Many chemical pumps are available with explosion-proof motors and ATEX certification for use in hazardous (classified) areas. Confirm with the manufacturer that the pump meets all relevant safety standards for your installation.
How often should chemical pumps be maintained?
Maintenance frequency depends on pump type, service conditions, and manufacturer recommendations. Routine inspections of seals, bearings, and impellers can prevent unexpected failures and extend pump life.
Where can I buy replacement parts for chemical pumps?
Most reputable chemical pump suppliers and manufacturers offer genuine replacement parts and maintenance kits. Use only OEM parts to ensure chemical compatibility and preserve warranty coverage.
Conclusion: Invest in the Right Chemical Pump for Your Process
Selecting the right chemical pump is crucial for process safety, efficiency, and regulatory compliance. By carefully considering chemical compatibility, operating conditions, pump type, and supplier expertise, you can ensure reliable fluid transfer in your facility—whether you are in chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, water treatment, or another demanding industry. For help with pump selection, technical questions, or to request quotes, contact our featured chemical pump manufacturers today.
Still have questions? Try searching: “chemical pump selection guide”, “chemical pump troubleshooting tips”, or “chemical pump suppliers near me” to find more information and connect with industry experts.


 Ball Valves
Ball Valves Butterfly Valves
Butterfly Valves Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal Pumps Check Valves
Check Valves Diaphragm Valves
Diaphragm Valves Flow Meters
Flow Meters Hydraulic Pumps
Hydraulic Pumps Hydraulic Valves
Hydraulic Valves Metering Pumps
Metering Pumps Solenoid Valves
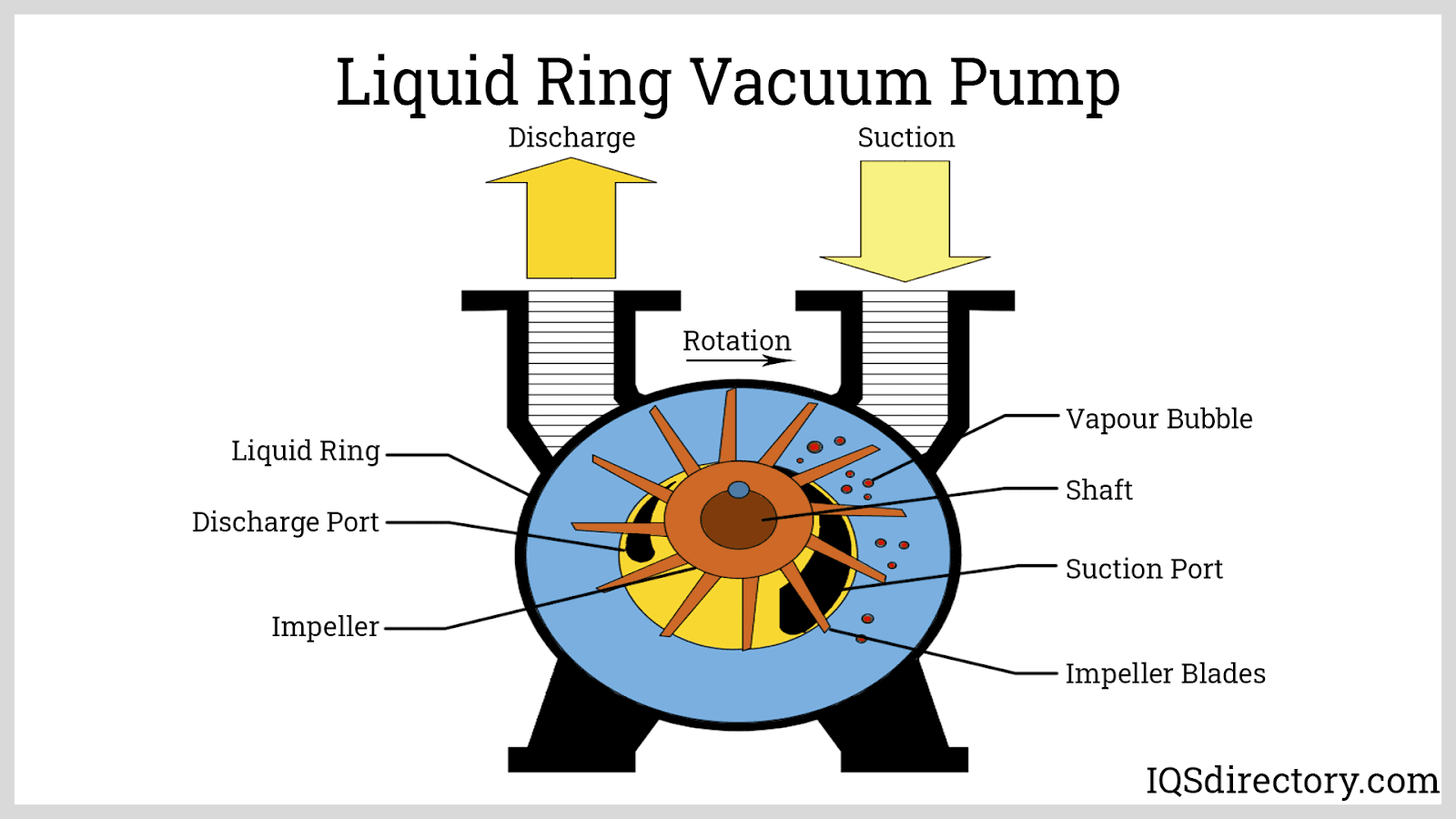
Solenoid Valves Vacuum Pumps
Vacuum Pumps Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services